Instrumentation R&D
Instrumented Baffle for Virgo
Instrumented Baffle for Virgo
As main hardware contribution to AdV+ by 2024, IFAE proposed the construction of new baffles instrumented with photo sensors around the test masses in the suspended areas. The implementation of active baffles with photo sensors, determining online the distribution of light close to the mirrors would allow for: a much more efficient alignment and fine-tune of the parameters of the interferometer during the commissioning phase after each shutdown period; feeding back the observed light distributions into the simulations and the description of the mirror surface; and the identification of developing high modes in the interferometer, beyond its fundamental mode, leading to recognizable patterns in the light distribution in the baffles. The proposed contribution to Virgo has recently drawn the attention of the LIGO community for the long-term future.
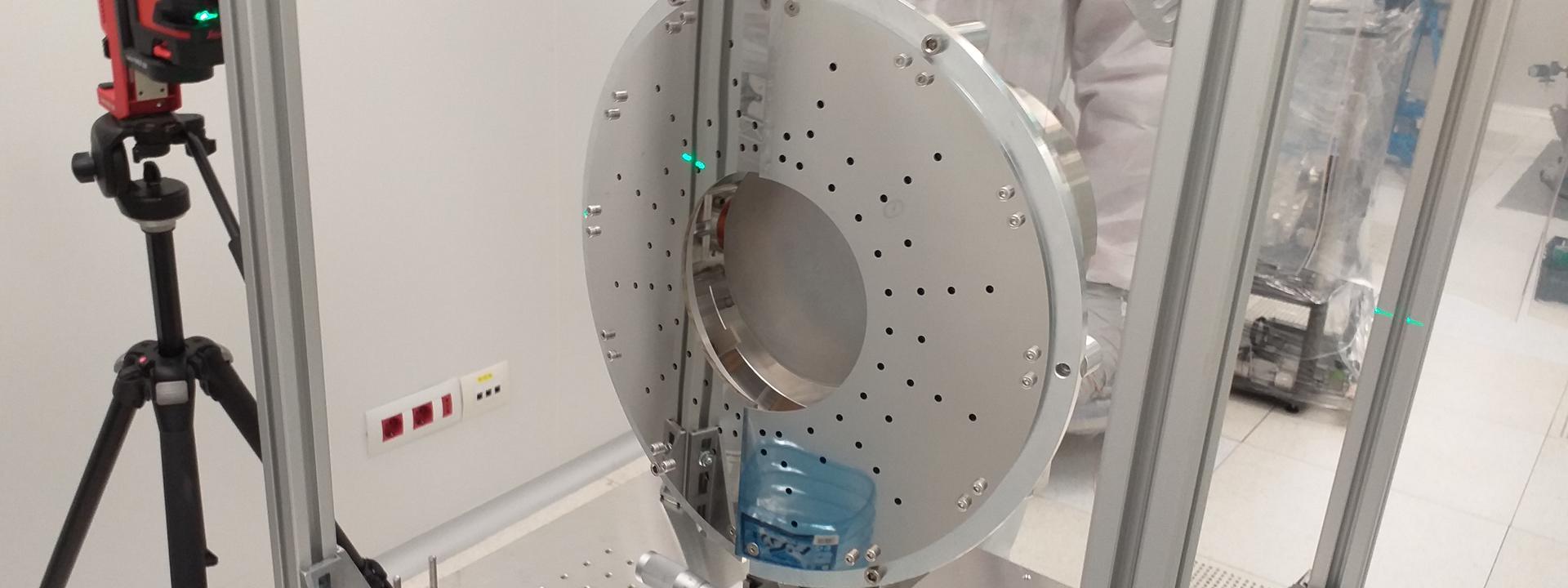
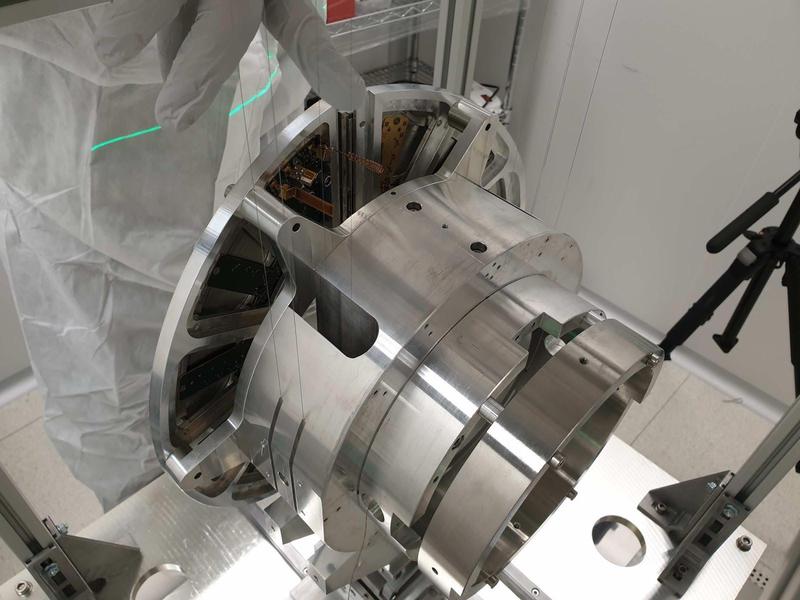
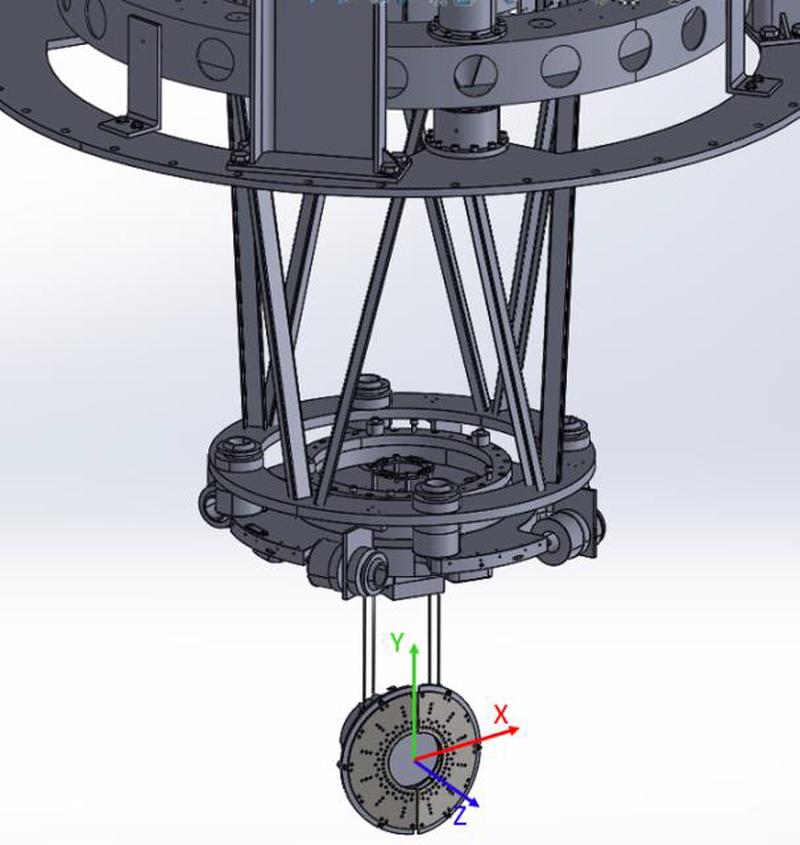
A prototype is being built at IFAE in time for summer 2020, when the suspended end mirror in the Input Mode Cleaner cavity of Virgo will be replaced and the corresponding payload reworked. This opens the opportunity to replace the passive baffle surrounding the mirror with an instrumented one, thus acting as a demonstrator of the technology. Figure 1 presents the current design.
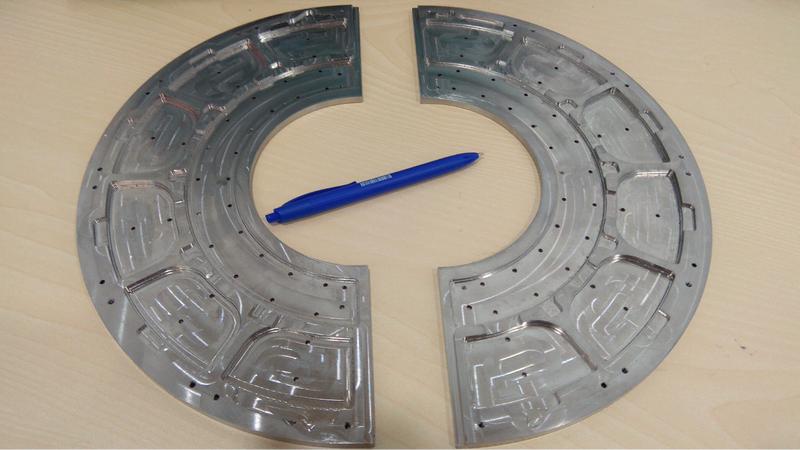
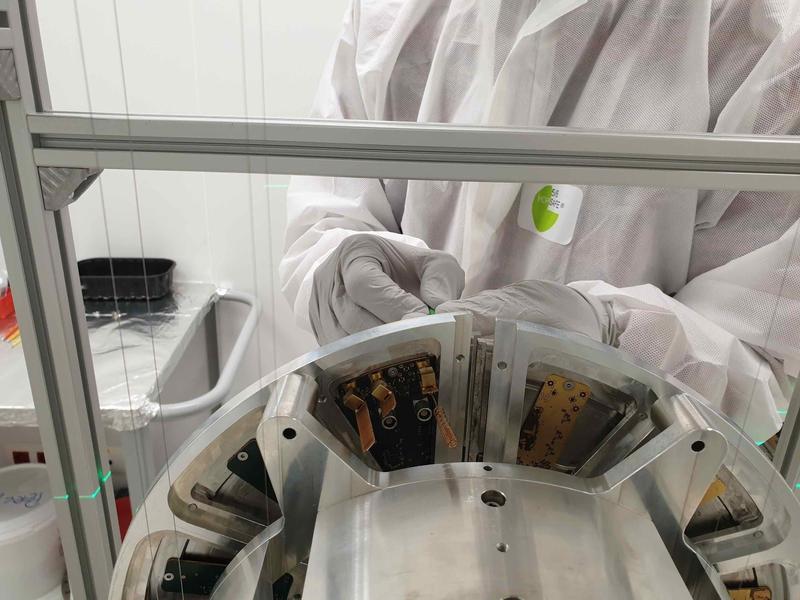
In 2019, an ad hoc R&D research line was placed in collaboration with Hamamatsu to develop a Si-based solution for an anti-reflecting IR photo-sensor that could work under Virgo conditions (ultra high vacuum and the absence of cooling). Similarly, special R&D was made to achieve edgeless apertures for the sensors in the coated stainless steel (thus minimizing the induced scattering in edges) and to determine the feasibility of a wireless readout (thus avoiding as much as possible cables running throughout the suspension system). In Fall 2019, the design was completed and the corresponding Conceptual Design Report passed successfully the Production Readiness Review carried out internally at Virgo.