Highlight
Qilimanjaro Quantum Tech, the spin-off of the UB, the BSC and the IFAE, pioneers quantum computing in Europe
July 29, 2020
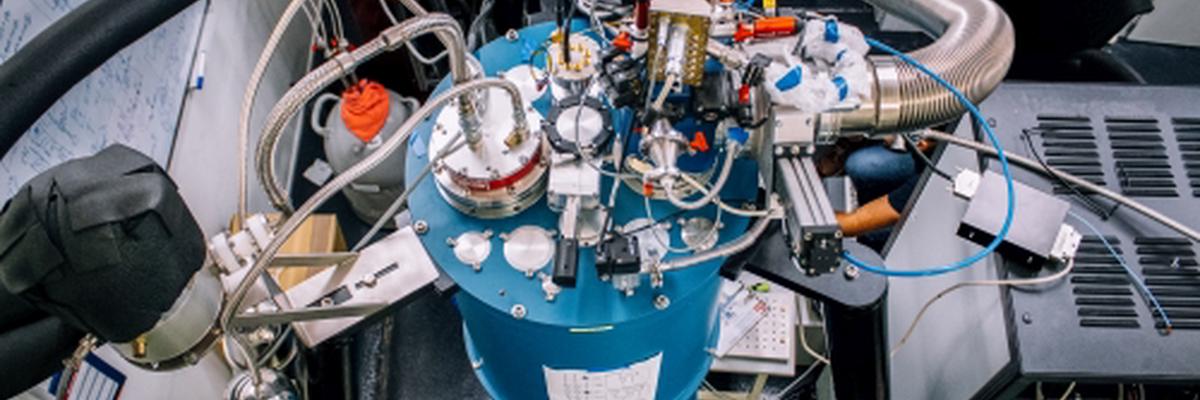

Quantum computing, a new technology with great transformative potential, is coming into our lives faster than we anticipated and, in less than a decade, it might completely transform the way in which we process information.
A team of researchers led by Prof. José Ignacio Latorre, from the Faculty of Physics of the University of Barcelona (UB), and including Dr. Pol Forn Díaz, from the Institute for High Energy Physics (IFAE), and Dr. Artur Garcia, from the Barcelona Supercomputing Center (BSC), have created Qilimanjaro Quantum Tech SL, a spin-off of the University of Barcelona, the Barcelona Supercomputing Center, and the Institute for High Energy Physics. The founding team is completed by Victor Canivell and Jordi Blasco, who have executive experience in the IT and M&A sectors respectively. This innovative spin-off also has the support of world-leading advisors from the quantum technology sector.
Qilimanjaro has all the ingredients for success: a team of top-level researchers and high-potential technology within a privileged ecosystem. Through a unique combination of hardware and software, Qilimanjaro promotes a leading initiative in Europe. José Ignacio Latorre explains that, “in the long term, Qilimanjaro aims to be one of the companies that develops quantum computers, while at the same time offering quantum algorithmic solutions for other companies”. He adds, “we are currently focused on developing quantum algorithms and creating the necessary infrastructure for a quantum computer, including the design and manufacture of quantum chips”. Pol Forn explains that, “the differential feature of Qilimanjaro’s quantum hardware is that it is based on high quality quantum bits –or qubits– to perform calculations using adiabatic quantum computing, a technique with the potential to offer actual optimization applications in this early period of the quantum technology era”.
Cloud-Accessible Technology
The objective of this spin-off is to offer a complete service and democratize this revolutionary technology, since the new computer, a quantum variational device, will be accessible from a cloud service. This will allow companies and users to explore the possibility of applying quantum algorithms to real-life problems. Qilimanjaro develops the software needed to exploit the potential of quantum computing using tools such as the MareNostrum supercomputer. “The first steps of quantum computing will be made in contact with supercomputing centres that will allow us to complement such a new technology, which in our case will act as a speed booster for optimization problems,” adds Artur Garcia, from the BSC.
Fast start
Qilimanjaro has already signed two important contracts for over 3 million euros with international clients, and has been accepted to collaborate in the H2020 European project “AVaQus” on quantum computing, led by Dr. Pol Forn Díaz and the IFAE and recently selected for funding by the European Commission.
The future will be quantum
Technology companies highlight the strategic importance of quantum computing; proof of this is the exponential increase in investments in this sector. According to data provided by Deloitte –one of the world’s leading consulting firms– it is estimated that the quantum computing market will be worth tens of billions of dollars from 2030 onwards. Quantum computing will revolutionize society geopolitically and economically, and will potentially impact different areas of our lives: health, finance, cryptography, and security, among many others. We will see how this new generation of computers will create new industries and alter existing ones. For example, it will help us create new drugs, develop new materials, and improve vehicle navigation and the planning of all kinds of tasks in industry and society. “The advantages of quantum computing will benefit companies that need a lot of computing power, such as those in the chemical, pharmaceutical, and banking sectors,” explains Prof. Latorre, who adds, “end users will benefit from the advantages of this new technology, for example, when these new drugs materialize or when a better way of calculating investment risk becomes available.”
- IFAE Research group
- Quantum Computing Technologies Group
- Contact
